Kyrgyzstan is expanding its renewable energy sector, focusing on solar power as a major component of its clean energy strategy. While the country has long relied on its significant hydropower capacity, it is now strategically diversifying its energy mix by incorporating solar, wind, and other renewable technologies to enhance energy security and combat climate change.
The Drive Towards Diversification: Beyond Hydropower in Kyrgyzstan renewable energy
For years, hydropower has been the backbone of Kyrgyzstan’s energy system. However, a strategic shift is underway to build a more resilient and diversified grid. This transition involves actively developing new solar and wind power stations, signaling a clear commitment to increasing renewable capacity beyond traditional sources. This move aligns with a broader national goal to achieve 80% renewable energy generation by 2050, positioning the country as a key player in Central Asia’s clean energy transition.
Solar Power at the Forefront of the Kyrgyzstan renewable energy Transition
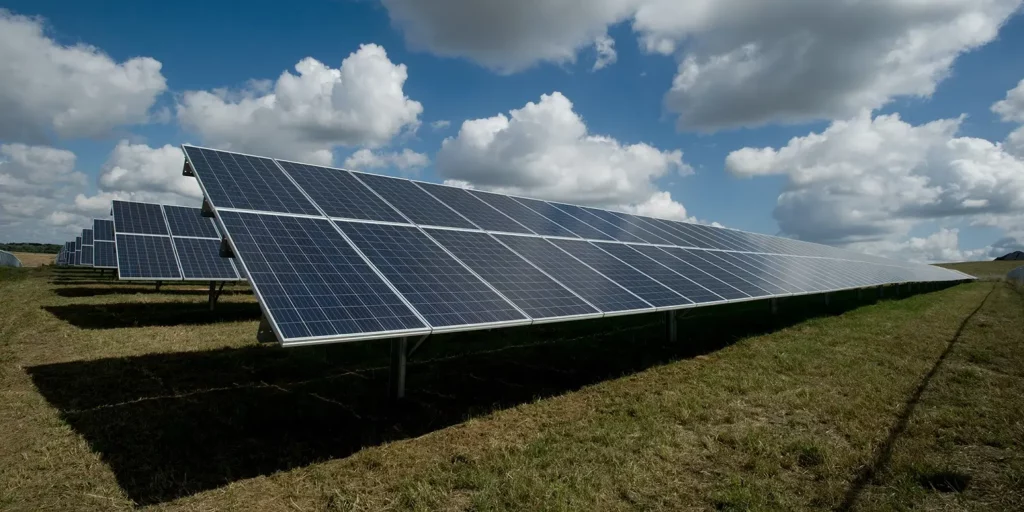
Solar energy is rapidly becoming a central pillar of Kyrgyzstan’s renewable ambitions. Supported by international partners, the country is making significant strides in developing utility-scale solar projects. A key initiative, the Solar Energy Project in Kyrgyzstan Advances with IFC, is setting the stage for increased private sector investment. This project includes the planned construction of two large solar power plants, each with a capacity of 100-150 MW, in the Batken and Talas regions.
These efforts are backed by substantial financial commitments. For instance, the Eurasian Development Bank (EDB) has announced a significant investment to support a new Kyrgyzstan solar power plant: $180M fuels impressive project. While large-scale projects are the primary focus, the groundwork being laid today could pave the way for future growth in local production, which requires a deep understanding of the solar panel manufacturing process and the associated plant cost breakdown.
Bolstering the Strategy with International Partnerships and Investment in Kyrgyzstan renewable energy
Kyrgyzstan’s clean energy journey is strongly supported by international cooperation and finance. The European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD) maintains an active portfolio in the country, with a remarkable 72% dedicated to sustainable infrastructure projects. This investment is crucial for developing the necessary framework for renewable energy deployment.
Furthermore, organizations like the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) are assisting Kyrgyzstan in integrating gender equality into its climate action plans, ensuring a just and inclusive transition. Building a sustainable energy sector also requires a skilled workforce, a need addressed by initiatives like the one where the OSCE Boosts Solar Energy in Kyrgyzstan with New Training. These partnerships help accelerate renewable deployment and enhance energy security across Central Asia.
The Bigger Picture: Hydropower and Future Potential for Kyrgyzstan renewable energy
Even as solar and wind gain momentum, hydropower remains a critical component of the regional energy landscape. The Kambarata-1 Hydropower Plant, a major project with a planned capacity of 1,860 MW, highlights the continued importance of hydropower in providing a stable, clean energy supply.
This multi-faceted approach—combining large-scale hydro with agile solar and wind projects—reflects a comprehensive strategy. The growing demand for clean energy creates a favorable environment for developing a domestic solar industry. A detailed Kyrgyzstan Solar Panel Manufacturing Report outlines the current landscape and future potential, emphasizing the importance of understanding the basics of solar panel manufacturing and the supply chain for key raw materials.
By embracing a diverse portfolio of renewable sources, fostering international partnerships, and investing in human capital, Kyrgyzstan is not just securing its own energy future but also contributing significantly to the greening of the entire Central Asian region.
If you’re interested in exploring the technical and financial aspects of creating a solar panel production line, consider enrolling in our free e-course on solar manufacturing.