Gain comprehensive insights into the statistics and metrics surrounding the solar production industry in Libya
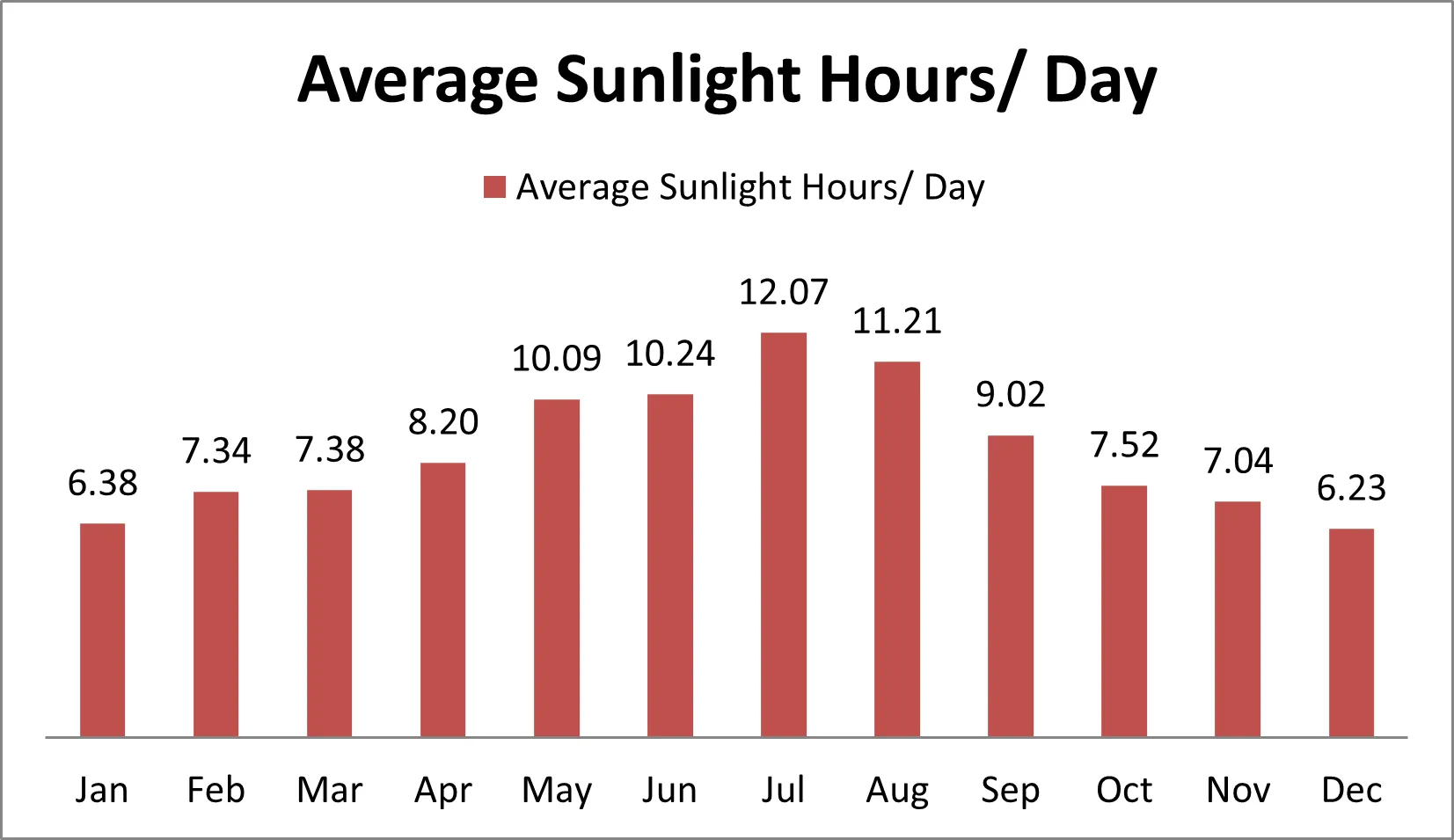
- Climate.Top. (2024). Sunshine & daylight hours in Tripoli, Libya: Sunlight, cloud & day length. Retrieved from https://www.climate.top/libya/tripoli-libya/sunlight/
- Murtaza, N., & Raza, M. (2023). Solar photovoltaic (PV) applications in Libya: Challenges, potential, opportunities and future perspectives. ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666790821002275
- GlobalPetrolPrices.com. (2024). Libya electricity prices, March 2024. Retrieved from https://www.globalpetrolprices.com/Libya/electricity_prices/
- Al-Soudani, M. (2021). Revitalizing operational reliability of the electrical energy system in Libya: Feasibility analysis of solar generation in local communities. ScienceDirect. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959652620336921
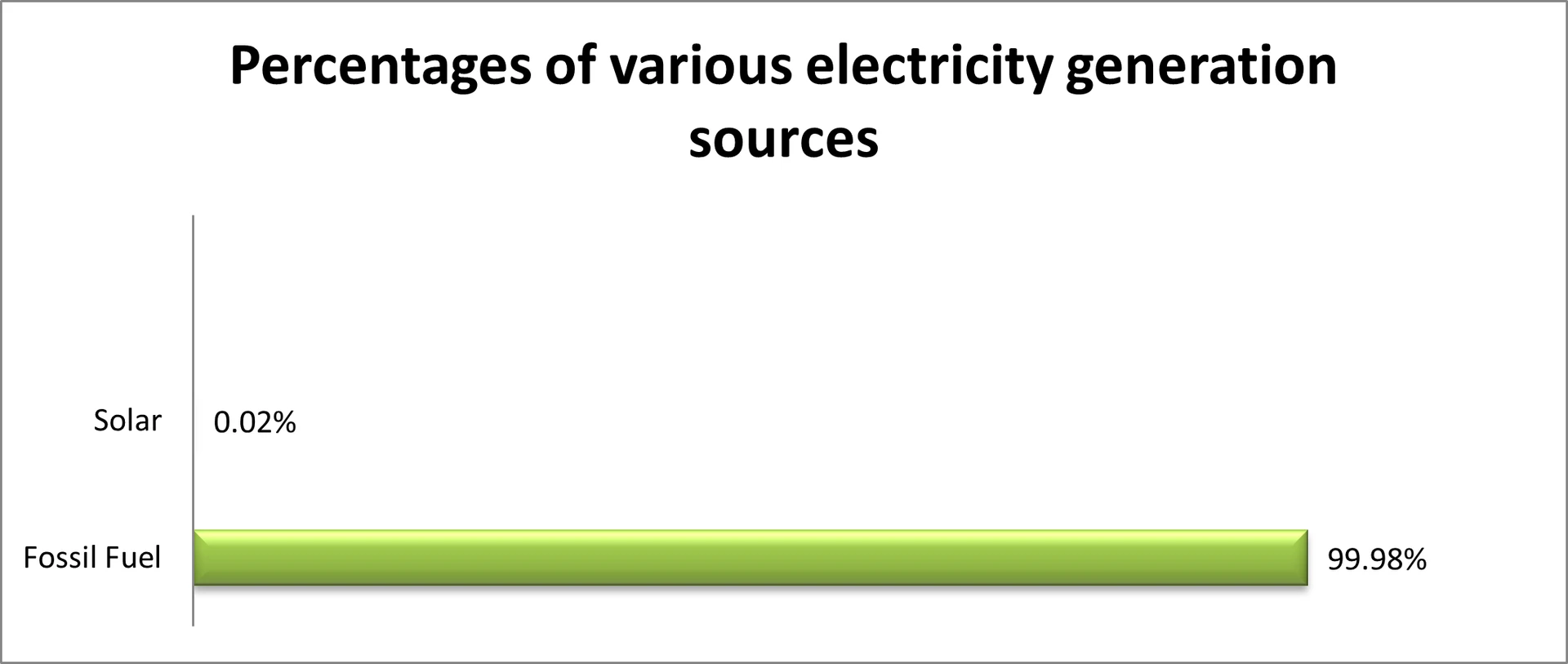
- International Renewable Energy Agency. (2024). Renewable energy statistics 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2023, from https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2024/Jul/IRENA_Renewable_Energy_Statistics_2024.pdf
- pv magazine International. (2024). TotalEnergies, Gecol to build 500 MW of solar in Libya. Retrieved from https://www.pv-magazine.com/2022/06/17/totalenergies-gecol-to-build-500-mw-of-solar-in-libya/
- Center for Strategic and International Studies. (2022). Blame it on the bitcoin: How cryptocurrency affects Libya’s electricity grid. Retrieved from https://www.csis.org/analysis/blame-it-bitcoin-how-cryptocurrency-affects-libyas-electricity-grid
- Worldometer. (2024). Libya electricity statistics. Retrieved from https://www.worldometers.info/electricity/libya-electricity/
- Africanews. (2024). Libyans celebrate end of chronic power cuts as electricity supply stabilizes. Retrieved from https://www.africanews.com/2023/09/03/libyans-celebrate-end-of-chronic-power-cuts-as-electricity-supply-stabilizes//
- U.S. Agency for International Development. (2024). Solar power is set to take off in Libya with USAID support. Retrieved from https://www.usaid.gov/libya/news/aug-13-2024-solar-power-set-takeoff-libya-usaid-support
- United Nations Development Programme. (2023). A step toward a greener future: Building Libya’s expertise on renewable energy. Retrieved from https://www.undp.org/arab-states/press-releases/step-toward-greener-future-building-libyas-expertise-renewable-energy
- OPEC Fund for International Development. (2024). UNDP solar power project in Libya helps save lives. Retrieved from https://opecfund.org/news/undp-solar-power-project-in-libya-helps-save-lives
- Power Technology. (2024). Power plant profile: Ghadames Solar PV Park, Libya. Retrieved from https://www.power-technology.com/data-insights/power-plant-profile-ghadames-solar-pv-park-libya/
- Power Technology. (2024). Power plant profile: Al-Sadada Solar PV Park, Libya. Retrieved from https://www.power-technology.com/data-insights/power-plant-profile-al-sadada-solar-pv-park-libya/
- Oxford Business Group. (2024). Misrata, Libya looks to renewables to meet growing energy demand. Retrieved from https://oxfordbusinessgroup.com/reports/libya/2024-report/energy-construction-infrastructure/renewable-energy-analysis/
- Oxford Academic. (2024). Assessment of the impact of a 10-MW grid-tied solar system on the Libyan grid in terms of the power-protection system stability. Clean Energy, 7(2), 389-394. https://academic.oup.com/ce/article/7/2/389/7093193
- World Salaries. (2024). Average solar engineer salary in Libya. Retrieved from https://worldsalaries.com/average-solar-engineer-salary-in-libya/
- Worldometer. (2024). Libya population. Retrieved from https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/libya-population/
- OpenSooq. (2024). Commercial warehouses for rent in Libya: Great deals. Retrieved from https://ly.opensooq.com/en/real-estate-for-rent/warehouses-for-rent
- Regus. (2024). Serviced office space in Libya | Offices for rent. Retrieved from https://www.regus.com/en-gb/libya
- Wikipedia. (2024). Energy in Libya. Retrieved from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy_in_Libya
- ResearchGate. (2021). The Libyan transmission network. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/figure/the-Libyan-transmission-network_fig1_328268680
- Trading Economics. (2024). Libya – Access to electricity (% of population). Retrieved from https://tradingeconomics.com/libya/access-to-electricity-percent-of-population-wb-data.html
- Observatory of Economic Complexity. (2024). Libya (LBY) exports, imports, and trade partners. Retrieved from https://oec.world/en/profile/country/lby%23latest-data&
- Libya Tribune. (2024). Renewable energies and green hydrogen in Libya – The legal framework. Retrieved from https://en.minbarlibya.org/2023/02/03/renewable-energies-and-green-hydrogen-in-libya-the-legal-framework/
- International Energy Agency. (2024). Law No. 426 establishing the Renewable Energy Authority of Libya (REAOL). Retrieved from https://www.iea.org/policies/4950-law-no-426-establishing-the-renewable-energy-authority-of-libya-reaol
- Energy Capital Power. (2024). Libya adopts renewable energy strategy, targets 20% by 2035. Retrieved from https://energycapitalpower.com/libya-adopts-renewable-energy-strategy-targets-20-by-2035/
- Libya Herald. (2024). “De-risking foreign investments for renewable energy in Libya” workshop. Retrieved from https://libyaherald.com/2024/03/de-risking-foreign-investments-for-renewable-energy-in-libya-workshop/