An entrepreneur invests in establishing a modern solar module assembly line in Ecuador, equipped with state-of-the-art machinery. The factory is ready, the team is trained, and the first modules are produced.
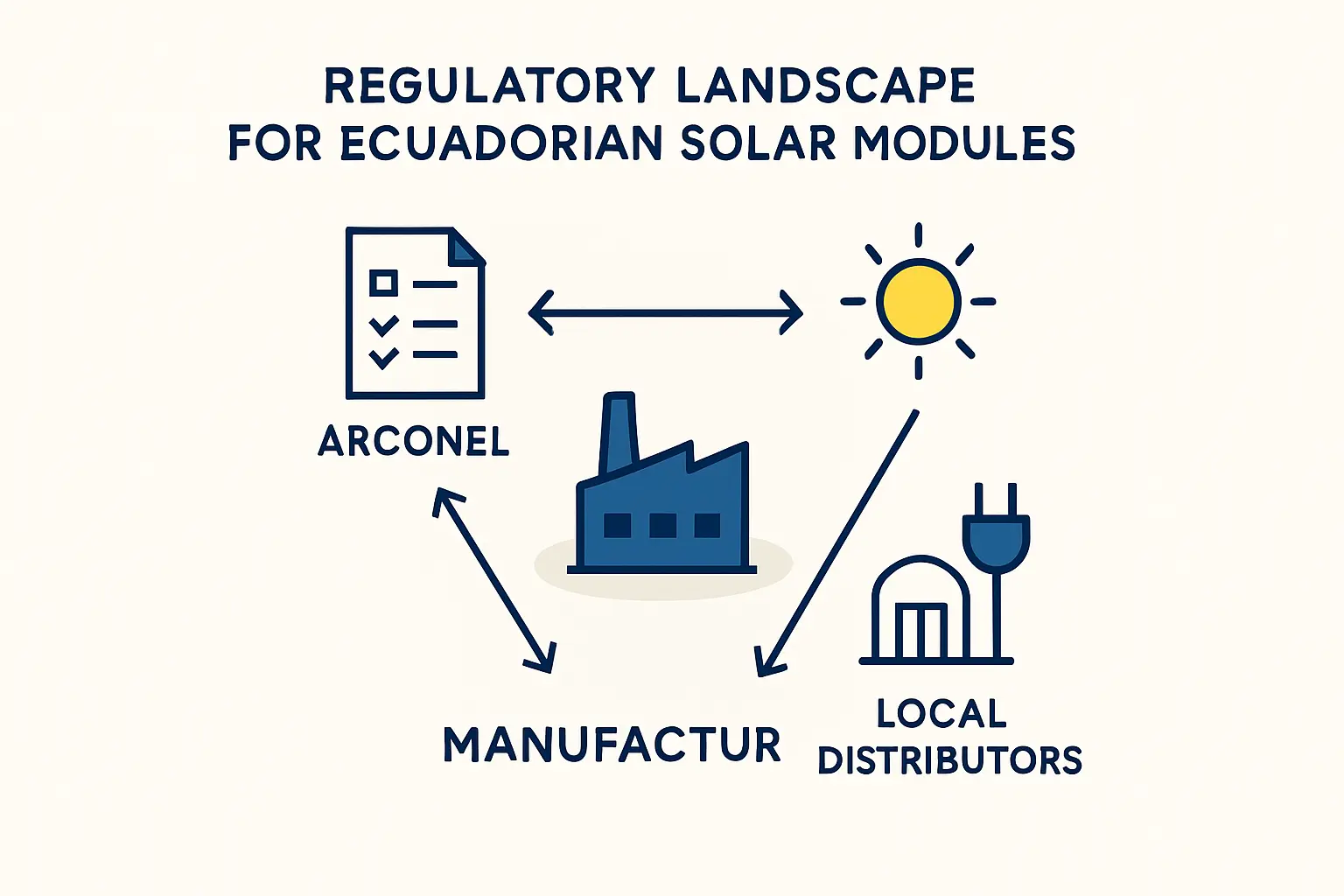
However, when the sales team approaches local distributors and project developers, they encounter a significant hurdle: a request for ARCONEL certification. Without this approval, their locally produced modules cannot be sold on the domestic market, halting the business before it even begins.
This scenario highlights a critical reality for any investor in Ecuador’s solar sector: manufacturing excellence alone is insufficient. Navigating the national regulatory landscape is essential for market entry. For solar modules, this means complying with the standards set by the Agency for the Regulation and Control of Energy and Non-Renewable Natural Resources (ARCONEL).
This article provides a clear overview of the ARCONEL requirements for photovoltaic (PV) modules, focusing on the essential INEN-IEC 61215 standard. It explains the purpose of the tests, outlines the compliance process, and details why meeting these standards is a strategic business imperative.
What is the ARCONEL Standard for Solar Modules?
ARCONEL, as the governing body for Ecuador’s energy sector, does not create its standards in isolation. Instead, it adopts globally recognized benchmarks to ensure safety, quality, and reliability. For crystalline silicon solar modules—the most common type manufactured globally—ARCONEL mandates compliance with the standard INEN-IEC 61215.
This designation may seem technical, but its components are straightforward:
-
IEC 61215: This is the core international standard developed by the International Electrotechnical Commission. It serves as the global benchmark for the ‘design qualification and type approval’ of terrestrial solar modules.
-
INEN: This prefix indicates that the standard has been officially adopted by the Servicio Ecuatoriano de Normalización (Ecuadorian Standardization Service), making it national law.
In essence, INEN-IEC 61215 is not a mere suggestion; it is a rigorous testing protocol that a solar module design must pass to be legally sold and installed in Ecuador. It serves as a comprehensive quality assurance check, verifying that the module will perform reliably and safely over its expected 25-year-plus lifespan. Understanding the fundamentals of international solar panel certifications provides a broader context for these national requirements.
The Core Components of INEN-IEC 61215 Testing
The certification process involves subjecting sample modules to a series of demanding tests that simulate real-world conditions. These tests can be grouped into three main categories, each designed to answer a crucial question for the end-user.
Ready to make big Profits?
The solar Industry is Booming
WE HELP NEWCOMERS to the solar industry start their own solar module production line. Customers can make BIG PROFITS by selling modules and finding investors, without wasting money and time on things they don't need!
1. Performance and Safety Verification
These initial tests confirm that the module operates as specified and poses no electrical risk. Key evaluations include:
Maximum Power Determination: Does the module produce the wattage advertised on its datasheet under standard test conditions? This is fundamental to a project’s financial model.
Insulation and Wet Leakage Current Tests: These safety-critical tests verify the module’s electrical insulation, ensuring it does not create a risk of electric shock, especially in wet conditions like rain or morning dew.
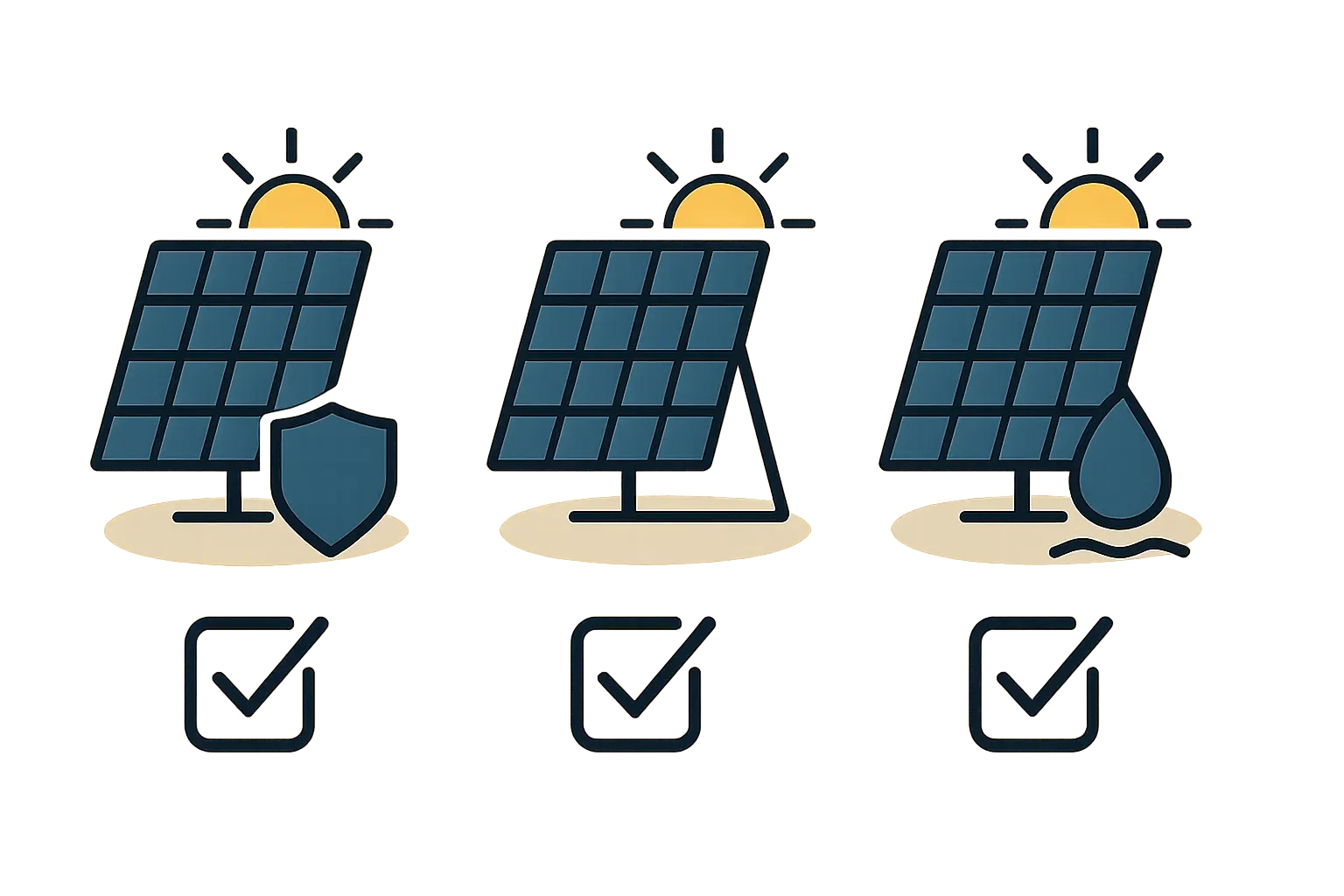
2. Durability and Environmental Stress Testing
This is the most intensive part of the qualification. The goal is to accelerate the aging process by simulating decades of exposure to harsh environmental factors. This is crucial in a country with diverse climates like Ecuador, from the hot and humid coast to the high-altitude, high-UV environment of the Andes.
Thermal Cycling Test: Modules are subjected to hundreds of cycles between extreme high and low temperatures (e.g., +85°C to -40°C) to simulate the stress of daily and seasonal temperature swings.
Damp-Heat Test: The module endures 1,000 hours in a chamber at 85°C and 85% relative humidity to test its resistance to moisture ingress, which can cause corrosion and delamination.
UV Preconditioning Test: This exposes the module to intense ultraviolet radiation to check for material degradation, such as backsheet yellowing or cracking.
Hot-Spot Endurance Test: This test ensures that if a single cell is partially shaded (e.g., by a leaf or bird dropping), it does not overheat and cause a fire or irreversible damage to the module.
3. Mechanical Strength and Build Quality
Finally, the tests verify the module’s physical resilience against forces it will encounter during transportation, installation, and its operational life.
Mechanical Load Test: The module is subjected to heavy pressure on its front and back surfaces to simulate the forces of strong winds or, in some regions, snow accumulation.
Robustness of Terminations Test: This ensures that the junction box, cables, and connectors are securely attached and can withstand the pulling and twisting forces common during installation.
Experience from J.v.G. turnkey projects shows that selecting production and testing equipment for a solar factory that not only meets but exceeds minimum requirements is a sound strategy for building a reputation for superior product durability.
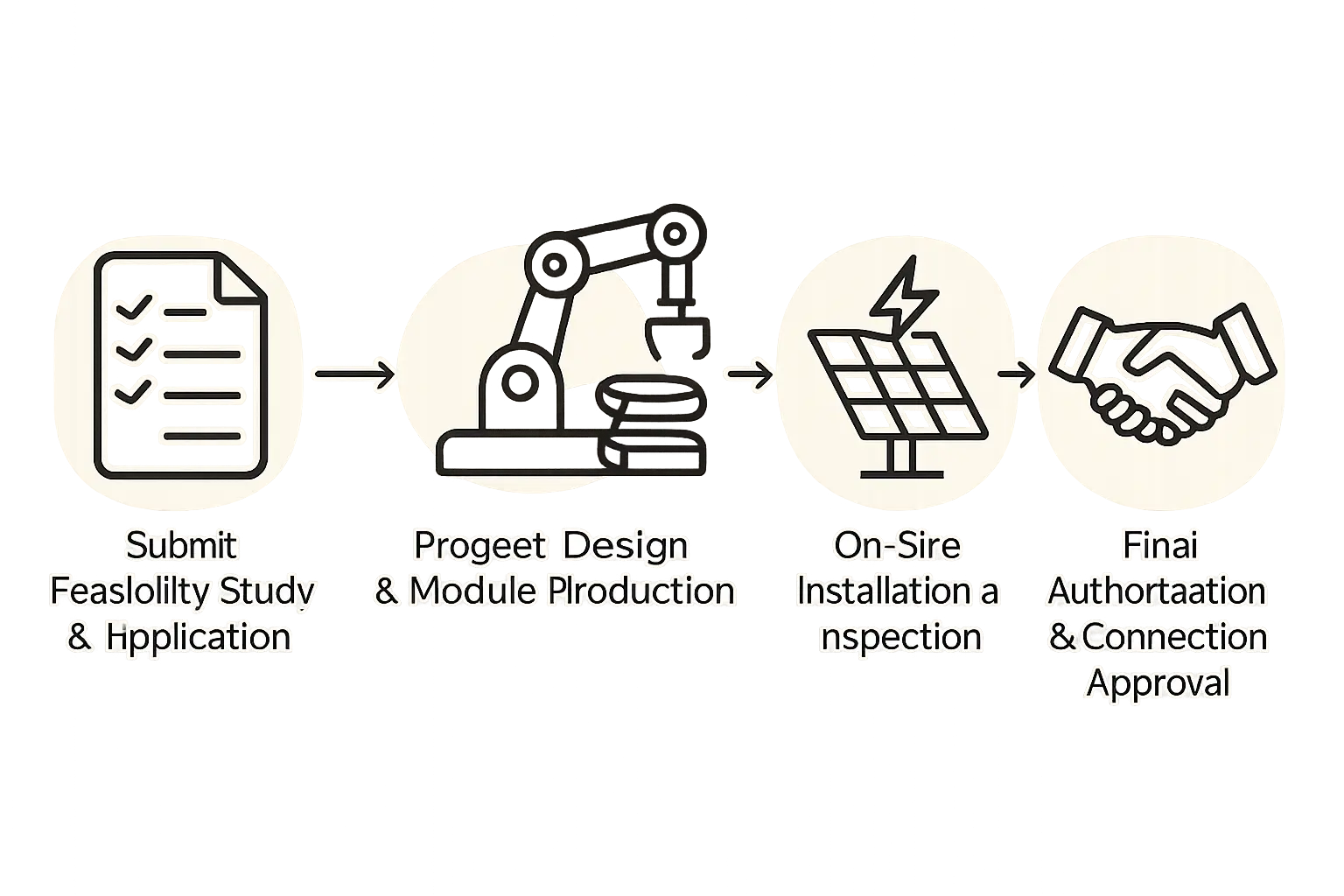
The Path to ARCONEL Compliance: A Step-by-Step Overview
Achieving certification is a structured process that must be integrated into a manufacturer’s operations from the very beginning.
Step 1: Design and Bill of Materials (BOM) Selection
Compliance starts on the drawing board. The choice of every component—from the solar cells and EVA encapsulant to the backsheet and junction box—must be made with the rigors of IEC 61215 testing in mind. Using pre-certified components from reputable suppliers is a critical first step.
Step 2: Type Testing at an Accredited Laboratory
A set of sample modules from a production run must be sent to an independent, accredited testing laboratory. This third-party laboratory will perform the full sequence of INEN-IEC 61215 tests.
Step 3: Certification and Documentation
Upon successful completion of all tests, the laboratory and an associated certification body will issue a formal certificate and test report. This documentation is the official proof of compliance that ARCONEL and potential customers require.
Step 4: Maintaining Compliance through Quality Management
Certification is not a one-time event. A manufacturer must maintain a robust Quality Management System (QMS), such as ISO 9001, to ensure every module produced is of the same quality as the certified model. Certification bodies typically conduct periodic factory inspections to verify ongoing compliance.
Why ARCONEL Compliance Is a Business Imperative
For an entrepreneur, viewing the INEN-IEC 61215 standard as a bureaucratic obstacle is a strategic error. Instead, it’s a key that unlocks the market and builds a sustainable business.
-
Market Access: It is the non-negotiable license to operate and sell within Ecuador’s formal energy sector.
-
Consumer Trust: Certification provides third-party validation of product quality and safety, building credibility for a new, local brand against established international competitors.
-
Project Eligibility: Government tenders, utility-scale developments, and commercial projects financed by banks almost universally mandate the use of ARCONEL-compliant modules.
-
Reduced Business Risk: A certified product is a reliable product. This significantly lowers the risk of widespread failures, costly warranty claims, and reputational damage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: How long does the IEC 61215 certification process typically take?
The full testing sequence can take several months, often between four to six, depending on the laboratory’s schedule and the specific tests involved. Planning for this timeline is essential.
Q2: What is the difference between IEC 61215 and INEN-IEC 61215?
Functionally, there is very little difference. INEN-IEC 61215 is the official Ecuadorian adoption of the international IEC 61215 standard. The test procedures and requirements are identical.
Q3: Can a manufacturer use components from any supplier?
While possible, it is highly inadvisable. Using components (e.g., backsheets, junction boxes) that are already certified to relevant IEC standards dramatically increases the probability of passing the full module certification on the first attempt. A change in any critical component requires a partial or full re-certification.
Q4: Is this certification valid for exporting modules from Ecuador?
IEC 61215 certification is the foundation for market access in many countries worldwide. However, some regions may have additional requirements (e.g., UL certification for the United States or CEC for Australia). Nonetheless, holding IEC 61215 is a powerful starting point for any export strategy.
Planning Your Production for Compliance
Successfully entering the Ecuadorian solar market requires balancing production efficiency with regulatory adherence. The requirements of ARCONEL and the INEN-IEC 61215 standard should be a central part of the initial solar factory planning process.
By integrating a compliance strategy from day one—through careful component selection, robust in-house quality control, and a clear understanding of the certification timeline—a new manufacturer can avoid costly delays and build a brand known for quality, safety, and trust. While the process is detailed, it offers a clear path to establishing a reputable and successful solar module manufacturing business in Ecuador.