For an entrepreneur considering a new solar module factory in Ecuador, a glance at the map reveals three prominent economic centers: Quito, Guayaquil, and Cuenca. While all appear viable at first glance, the choice of location is one of the most critical decisions in the venture.
This decision will influence everything from supply chain efficiency and production costs to the availability of a skilled workforce for decades to come. An incorrect choice can lead to unforeseen logistical bottlenecks and operational expenses that erode profitability before the first module is produced.
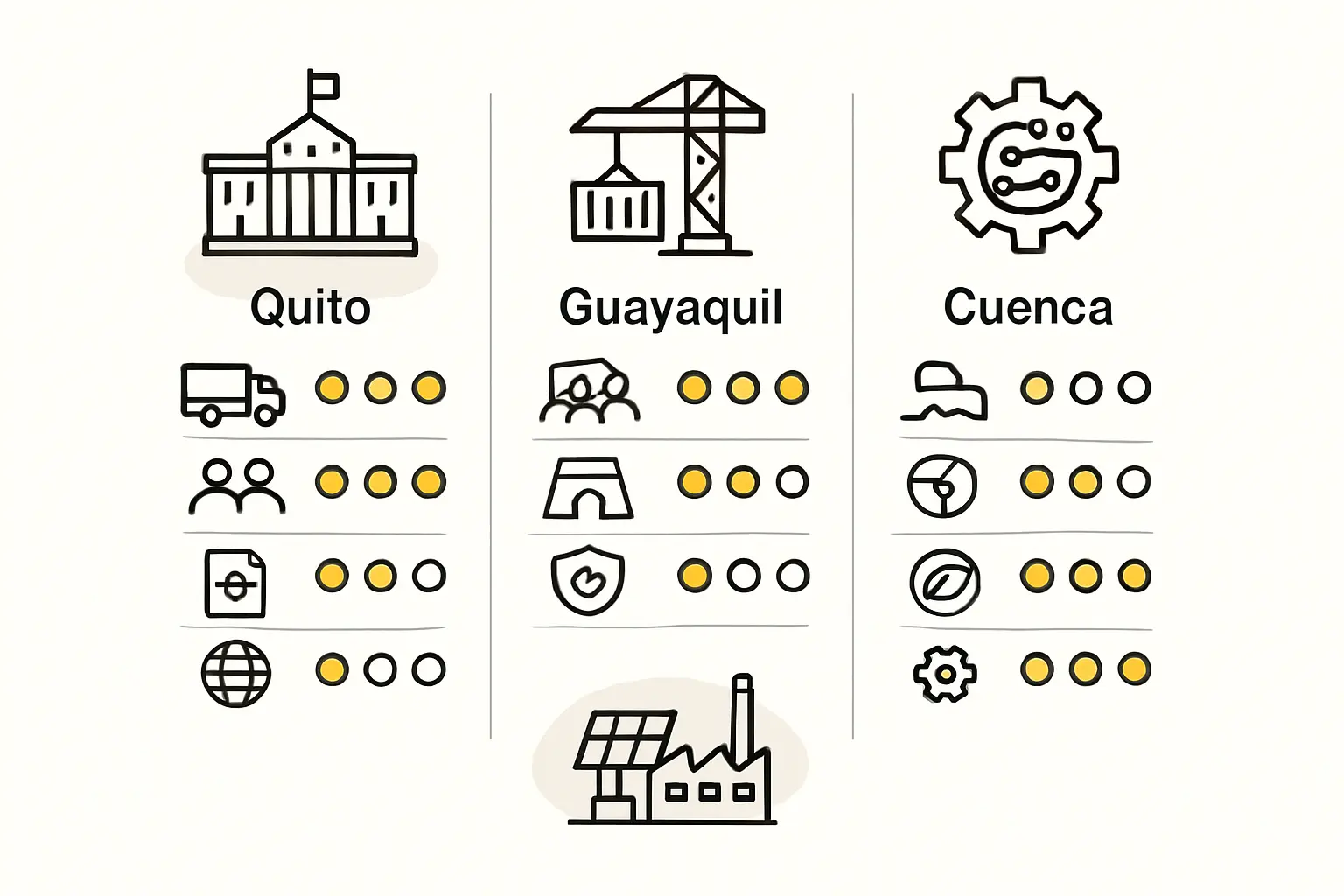
This article provides a comparative analysis of Ecuador’s three main industrial hubs, examining the key factors an investor must consider—logistics, labor, the operational environment, and strategic advantages—to select the optimal site for a new solar panel manufacturing facility.
The Strategic Importance of Site Selection
Choosing a location is not merely about finding an available plot of land; it is the foundational step that determines the long-term operational viability and competitiveness of the factory. A well-chosen site optimizes the flow of raw materials and finished products, minimizes transport costs, and ensures access to the right talent.
This decision directly impacts the overall investment for solar panel manufacturing by shaping recurring costs for logistics and labor. A comprehensive understanding of each location’s unique profile is essential for anyone learning how to start a solar panel factory and building a sustainable business model.
An Overview of Ecuador’s Industrial Landscape
Ecuador presents a compelling case for investment in renewable energy manufacturing, supported by a dollarized economy that eliminates currency exchange risk and a government actively promoting sustainable energy sources. The country’s infrastructure, particularly its road and port systems, has seen significant modernization.
The nation’s primary industrial activity is concentrated around three key cities. Each of these hubs—Quito, Guayaquil, and Cuenca—offers a distinct combination of advantages and challenges that must be carefully weighed against the specific goals of a solar manufacturing project.
Deep Dive: Quito (Pichincha Province)
Located high in the Andes at an altitude of 2,850 meters, Quito is the political and administrative capital of Ecuador. Its industrial zones, such as the Parque Industrial Itulcachi and Calacalí, cater to a diverse range of industries.

Ready to make big Profits?
The solar Industry is Booming
WE HELP NEWCOMERS to the solar industry start their own solar module production line. Customers can make BIG PROFITS by selling modules and finding investors, without wasting money and time on things they don't need!
Logistics and Infrastructure
Quito is home to the Mariscal Sucre International Airport (UIO), a modern air cargo hub. For sea freight, however, the closest major port is Esmeraldas, a 6-to-8-hour truck journey away.
This significant overland distance is a major logistical factor for any business reliant on importing raw materials or exporting finished goods. The high altitude can also subtly affect the performance of certain machinery and increase energy consumption for climate control.
Labor and Talent Pool
As the nation’s capital, Quito boasts the highest concentration of universities and technical institutes. This translates into a deep pool of skilled professionals, engineers, and administrative talent. For a solar factory requiring R&D personnel or highly specialized technicians, Quito offers a distinct advantage.
Strategic Considerations for Solar Manufacturing
Pros: Access to a highly skilled and educated workforce; proximity to government bodies and financial institutions.
Cons: Significant distance to seaports, leading to higher transportation costs for materials and finished modules; higher operational costs (land, labor, services) compared to other regions.
A Quito-based factory is best suited for an operation that prioritizes access to top-tier talent and serves the domestic Andean market, where proximity to a seaport is less critical.
Deep Dive: Guayaquil (Guayas Province)
Guayaquil is Ecuador’s largest city and its undisputed economic and logistical powerhouse. Situated on the Pacific coast, its industrial areas, like Parque Industrial Inmaconsa along the Vía a Daule, are intrinsically linked to its port.
The Logistics Hub of Ecuador
The deep-water Port of Guayaquil is the country’s primary commercial gateway, handling over 70% of its import and export cargo. This direct access to global shipping lanes is a powerful advantage for a solar manufacturer. Raw materials like glass, EVA, and solar cells can be imported efficiently, and finished modules can be exported with minimal inland transportation.
Furthermore, proximity to Special Economic Development Zones (ZEDEs), such as the ZEDE del Litoral, can offer substantial tax and customs benefits, directly bolstering the venture’s financial model. The city’s José Joaquín de Olmedo International Airport (GYE) and extensive highway network further solidify its logistical dominance.
Climate and Manufacturing
The city’s hot and humid tropical climate presents a unique challenge. A solar module factory requires a strictly controlled environment to ensure the quality and longevity of the laminating process. This means a facility in Guayaquil would require a more robust and energy-intensive HVAC system compared to one in the highlands, a key consideration for the design of the solar panel production line.
Strategic Considerations for Solar Manufacturing
Pros: Unmatched logistical advantage for import/export; large industrial labor pool; potential for significant tax incentives via ZEDEs.
Cons: High humidity requires significant investment in climate control; higher security costs are also a common consideration in the region.
Guayaquil is the premier choice for an export-oriented manufacturing operation that plans to compete in international markets.
Deep Dive: Cuenca (Azuay Province)
Nestled in the southern Andes, Cuenca is renowned for its skilled artisans and a strong manufacturing culture. The Parque Industrial de Cuenca is a well-organized hub for businesses in assembly, ceramics, and furniture, among others.
A Hub of Skilled Manufacturing
Cuenca’s primary advantage is its workforce, known for precision, discipline, and a strong work ethic in assembly-line environments. This is highly relevant for solar module manufacturing, where manual dexterity and attention to detail are paramount.
Labor costs in Cuenca are generally lower than in Quito or Guayaquil, offering a potential competitive advantage. Operators for each solar panel manufacturing machine must be trained effectively, and Cuenca’s labor force has a proven track record in this area.

Logistics and Connectivity
Cuenca is not a primary logistics hub. It relies on the Port of Guayaquil, a 3-to-4-hour truck journey through the mountains. While this is a manageable distance, it adds a logistical layer and cost that must be factored into the business plan. The city has a small airport with domestic flights, but international cargo must be routed through Quito or Guayaquil.
Strategic Considerations for Solar Manufacturing
Pros: Access to a cost-effective and highly skilled manufacturing workforce; a well-established industrial culture and business-friendly municipal government.
Cons: Reliant on Guayaquil’s port, adding inland transport costs; smaller overall labor pool compared to the two larger cities.
Cuenca is an excellent candidate for a factory focused on high-quality assembly for the domestic or regional South American market, where the benefits of a skilled, cost-effective workforce can outweigh the logistical disadvantages.
Comparative Analysis: A Side-by-Side Look
The optimal choice ultimately depends on the business model. Based on J.v.G. Technology’s experience in guiding turnkey factory projects, aligning the site’s strengths with the company’s strategic priorities is paramount.
| City | Primary Advantage | Port Proximity | Labor Pool | Operating Costs | Best Suited For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Quito | Skilled professionals & R&D talent | Poor (6-8 hours to Esmeraldas) | Highly educated, higher cost | High | R&D-heavy, domestic focus |
| Guayaquil | Port logistics & export access | Excellent (direct access) | Large industrial, moderate cost | Moderate (higher climate control) | Export-oriented production |
| Cuenca | Skilled, cost-effective labor | Fair (3-4 hours to Guayaquil) | Skilled assembly, lower cost | Low | Quality-focused, regional supply |
FAQ: Common Questions on Site Selection in Ecuador
How critical is proximity to a port for a new solar factory?
For a business model centered on exports, proximity is essential. Inland transportation can add significant cost and complexity, eroding competitive pricing in the global market. For a factory serving only the domestic market, it becomes less of a priority.
How does the dollarized economy affect investment?
The use of the U.S. dollar simplifies financial planning and eliminates the risk of currency devaluation against major global currencies. This creates a stable and predictable environment for long-term investments, which is a significant benefit for foreign entrepreneurs.
Are there specific national incentives for solar manufacturing?
Ecuador has laws to promote investment, particularly in priority sectors like renewable energy. These can include income tax exemptions and duty-free importation of capital goods. The most significant benefits, however, are often found within Special Economic Development Zones (ZEDEs), which are predominantly located near major logistics hubs like Guayaquil.
What are the main bureaucratic challenges to consider?
Like many countries, Ecuador has its own bureaucratic processes for permits, licenses, and customs. Navigating these procedures can be a challenge for new investors. Engaging with experienced local partners or consultancy firms who understand the administrative landscape is crucial for a smooth project launch.
The selection of a factory site in Ecuador is a multifaceted decision with no single correct answer. A thorough evaluation of the business’s core strategy—whether it is geared toward export, domestic sales, innovation, or cost leadership—will illuminate the optimal path forward. Guayaquil offers the world a gateway, Quito provides the intellectual capital, and Cuenca delivers manufacturing excellence.