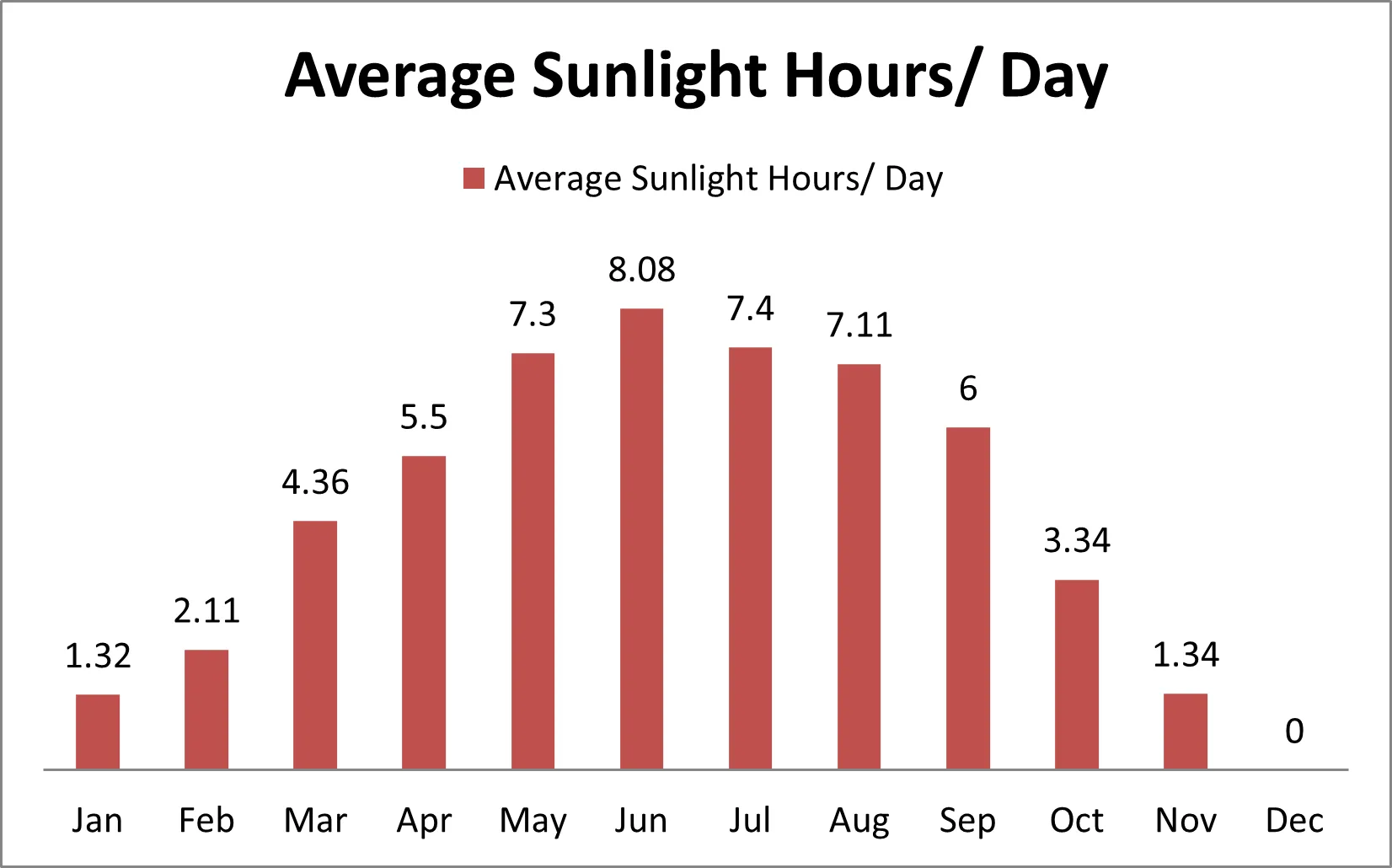
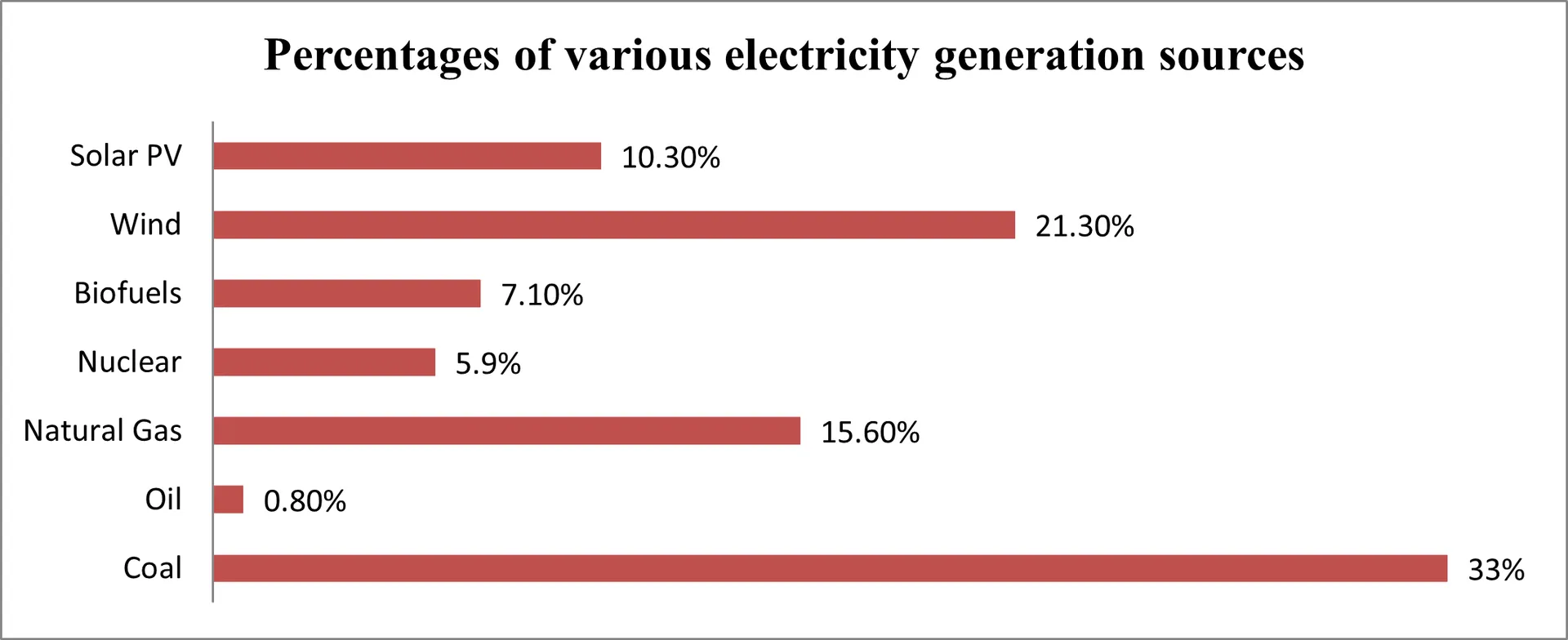
- Climate Top. (n.d.). Sunshine & daylight hours in Berlin, Germany. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://www.climate.top/germany/berlin/sunlight/
- Tritech Energy. (n.d.). kWp and kWh – this is what the photovoltaic key figures tell you. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://www.tritec-energy.com/en/guidebook/kwp-kwh-pv-key-figures/
- Wehrmann, B. (2024). Industry electricity prices for German companies drop almost one quarter in early 2024. Clean Energy Wire. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://www.cleanenergywire.org/news/industry-electricity-prices-german-companies-drop-almost-one-quarter-early-2024
- VDE. (2022). Power supply in Germany in 2022: Supply reliability at a very high level. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://www.vde.com/en/press/press-releases/stromversorgung-2022-in-deutschland-versorgungszuverlaessigkeit
- Spasić, V. (2024). Germany adds record 14 GW of solar in 2023 – half is on households. Balkan Green Energy News. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://balkangreenenergynews.com/germany-adds-record-14-gw-of-solar-in-2023-half-is-on-households/
- Mercom Staff. (2024). Daily news wrap: Germany 3.7 GW solar in Q1. Mercom India. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://www.mercomindia.com/daily-news-wrap-germany-3-7-gw-solar-q1
- Statista. (2023). Gas prices for household customers in Germany from 2013 to 2023. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1346386/gas-prices-development-household-customers-germany/
- German Institute in Taipei. (n.d.). Article 9 data. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://taipei.diplo.de/blob/2310622/59775cb0bc6f6aa8eecd2bee2c0a0a7f/artikel-9-data.pdf
- MIWI Institut. (2021). Full costs per kWh: Which is the cheapest energy source in Germany? Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://miwi-institut.de/archives/1591
- Wehrmann, B. (2024). Renewables will not reduce German electricity prices throughout next decade – govt advisor. Clean Energy Wire. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://www.cleanenergywire.org/news/renewables-will-not-reduce-german-electricity-prices-throughout-next-decade-govt-advisor
- International Energy Agency. (n.d.). Energy system of Germany. Retrieved May 7, 2024, from https://www.iea.org/countries/germany
- Appunn, K. (2020). 12 minutes per year: Germany has shortest time of power black-outs ever. Clean Energy Wire. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.cleanenergywire.org/news/12-minutes-year-germany-has-shortest-time-power-black-outs-ever
- EnergySage. (2023). Where is solar energy used the most worldwide? Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.energysage.com/about-clean-energy/solar/where-is-solar-energy-used/
- Amelang, S. (2024). Germany’s solar additions jump to new record of 1 million new systems in 2023. Clean Energy Wire. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.cleanenergywire.org/news/germanys-solar-additions-jump-new-record-1-million-new-systems-2023
- Climate Action Network Europe. (2024). Germany’s Solar Rooftop Country Profile. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://caneurope.org/content/uploads/2024/04/Germany-Residental-Rooftop-Solar-Country-Profile.pdf
- List Solar. (2021). Largest solar power parks in Germany. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://list.solar/plants/largest-plants/solar-plants-germany/
- Murray, C. (2023). RheinEnergie and Bayernwerk, Lechwerke launch BESS projects in Germany totaling 14 MWh. Energy Storage News. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.energy-storage.news/germany-utilities-rheinenergie-and-bayernwerk-launch-bess-projects/
- Glassdoor. (2023). Solar installer salaries in Germany. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.glassdoor.co.in/Salaries/germany-solar-installer-salary-SRCH_IL.0,7_IN96_KO8,23.htm
- Worldometer. (n.d.). Population of Germany. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/germany-population/
- Eco Watch. (2024). Solar panel cost guide in German, OH (2024 update). Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.ecowatch.com/solar/panel-cost/oh/german
- Wikipedia. (n.d.). Energy in Germany. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Energy_in_Germany
- Appunn, K., & Russell, R. (2021). Set-up and challenges of Germany’s power grid. Clean Energy Wire. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.cleanenergywire.org/factsheets/set-and-challenges-germanys-power-grid
- Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Climate Action. (n.d.). Grids and infrastructure. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.bmwk.de/Redaktion/EN/Artikel/Energy/electricity-grids-of-the-future-01.html
- Robinsun. (n.d.). The right to plug-in solar installations: Changes in property law make solar installations even easier in Germany. Robinsun. https://robinsun.com/blogs/news/the-right-to-plugin-solar-installations-changes-in-property-law-make-solar-installations-even-easier-in-germany
- AltEnergyMag. (2023, June). Solar around the world: Schemes and regulations in each country. AltEnergyMag. https://www.altenergymag.com/story/2023/06/solar-around-the-world-schemes-and-regulations-in-each-county/39661/
- Uibeleisen, M., & Groneberg, S. (2024). Overview of the main new solar regulation in Germany. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://www.mwe.com/insights/solar-package-1-overview-of-the-main-new-solar-regulation-in-germany/
- Solar Stone. (2023). Solar subsidies in Germany. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://solarstone.com/blog/solar-subsidies-in-germany
- ESFC. (2024). Investments in solar power plants in Germany: Photovoltaics on the rise. Retrieved May 8, 2024, from https://esfccompany.com/en/articles/news/investments-in-solar-power-plants-in-germany-photovoltaics-on-the-rise/
- Power Technology. (2024, September 9). Top five solar PV plants in development in Germany. Power Technology. Retrieved from: https://www.power-technology.com/data-insights/top-5-solar-pv-plants-in-development-in-germany/

Sign Up Below to Access Our FREE Solar Module Production E-Course