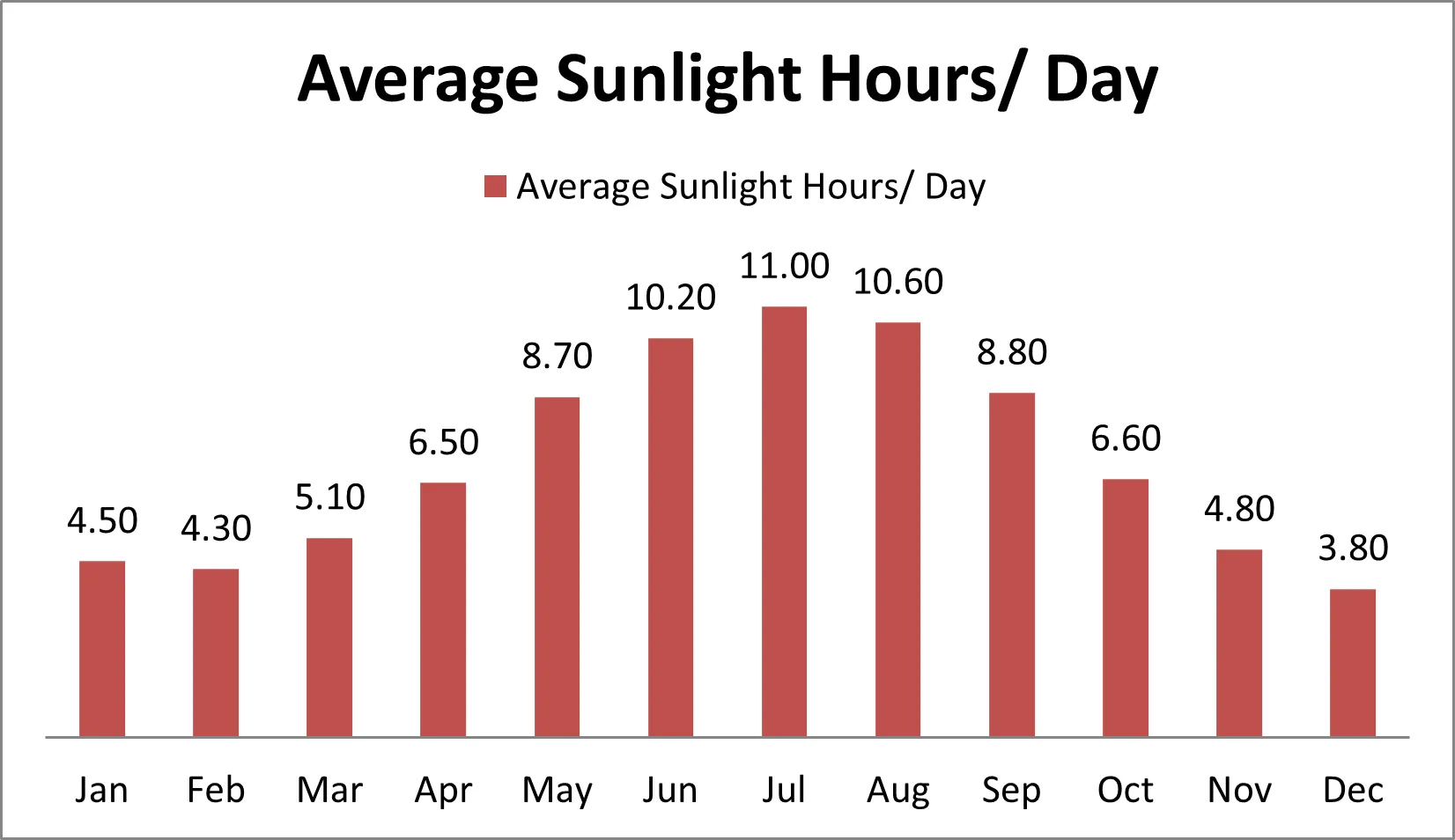
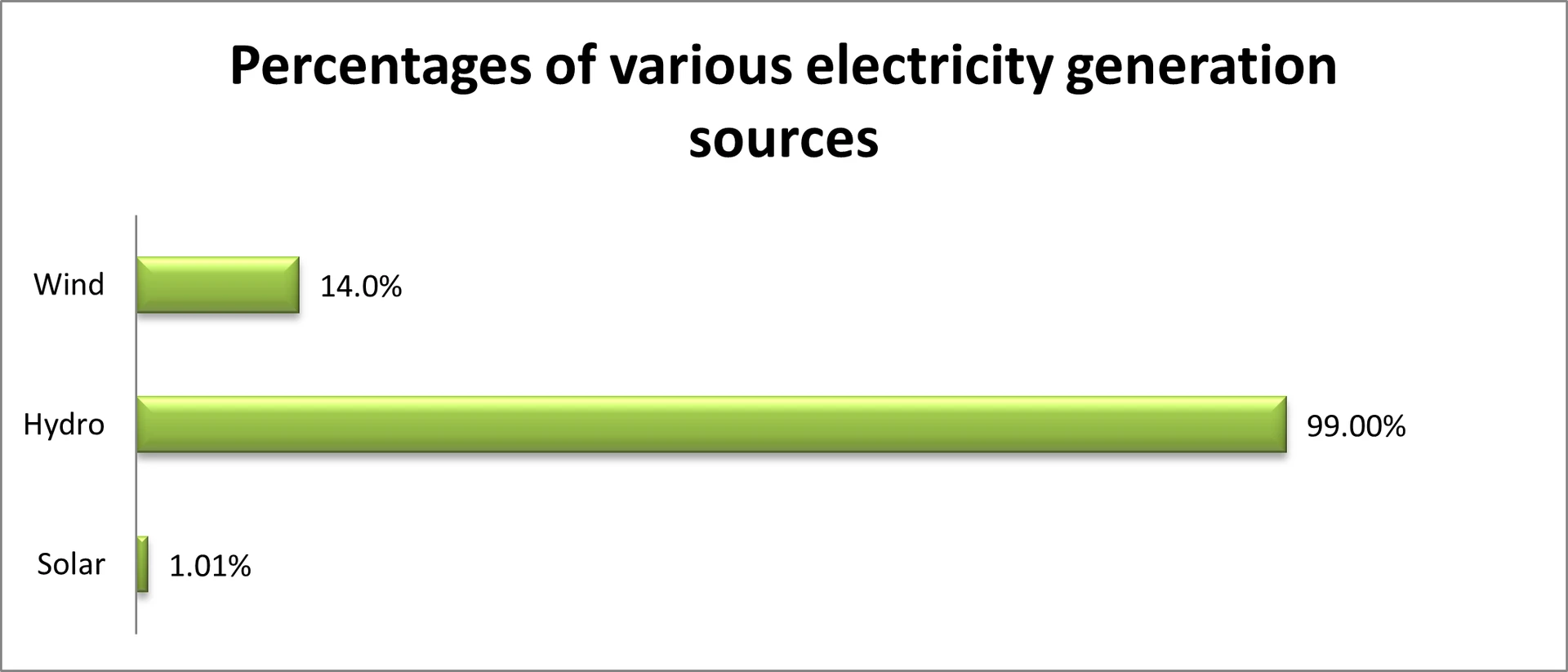
Gain comprehensive insights into the statistics and metrics surrounding the solar production industry in Nepal
- Climate.top. (2024). Sunshine & daylight hours in Kathmandu, Nepal sunlight, cloud & day length. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.climate.top/nepal/sunlight/
- Shreesha, G., Raut, D. B., & Khadka, S. (2022, October). Modeling, simulation, and performance analysis of large scale solar power plant in Nepal under single and double axis tracking systems. Proceedings of the 12th IOE Graduate Conference, Peer Reviewed, 12. Retrieved December 8, 2024, from https://conference.ioe.edu.np/publications/ioegc12/IOEGC-12-007-12012.pdf
- GlobalPetrolPrices.com. (2024, March). Nepal electricity prices. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.globalpetrolprices.com/Nepal/electricity_prices/
- Niroomand, N., & Jenkins, G. P. (2020, April). Estimation of households’ and businesses’ willingness to pay for improved reliability of electricity supply in Nepal. Energy for Sustainable Development, 55, 201-209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.esd.2020.02.002
- International Renewable Energy Agency. (2024). Renewable energy statistics 2024. Retrieved November 9, 2023, from https://www.irena.org/-/media/Files/IRENA/Agency/Publication/2024/Jul/IRENA_Renewable_Energy_Statistics_2024.pdf
- Neupane, D., Kafle, S., Karki, K. R., Kim, D. H., & Pradhan, P. (2022, January). Solar and wind energy potential assessment at provincial level in Nepal: Geospatial and economic analysis. Renewable Energy, 181, 278-291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2021.09.029
- Butchers, J., Williamson, S., Booker, J., Maitland, T., Karki, P. B., Pradhan, B. R., Pradhan, S. R., & Gautam, B. (2022). Cost estimation of micro-hydropower equipment in Nepal. Development Engineering, 7, 100097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.deveng.2022.100097
- Worldometer. (2024). Nepal electricity statistics. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.worldometers.info/electricity/nepal-electricity/
- Timilsina, G., & Steinbuks, J. (2021). Economic costs of electricity load shedding in Nepal. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 146, 111112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2021.111112
- Kafle, U., Anderson, T., & Lohani, S. P. (2023). The potential for rooftop photovoltaic systems in Nepal. Energies, 16(2), 747. https://doi.org/10.3390/en16020747
- The Himalayan Times. (2023). Solar energy for household consumption: Its financial feasibility. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://thehimalayantimes.com/opinion/solar-energy-for-household-consumption-its-financial-feasibility
- Department of Electricity Production. (2024). Power plants: Solar. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from http://www.doed.gov.np/license/56
- Investopaper. (2023). 17 solar power projects under construction in Nepal to produce 110 MW of electricity. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.investopaper.com/news/solar-power-projects-under-construction-in-nepal/
- Barefoot College. (2023, August 28). Remote Nepal village receives 45 solar systems. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.barefootcollege.org/45-solar-systems-installed-in-remote-village-of-nepal/
- EKOenergy ecolabel. (2023). Solar mini-grid for rural electrification in Nepal. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.ekoenergy.org/solar-minigrid-for-rural-electrification-in-nepal/
- WWF. (2023). Solar panels light up rural Nepal. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.wwf.mg/en/?19577/Solar-panels-light-up-rural-Nepal
- Alternative Energy Promotion Centre. (2023). Promotion of solar energy in rural and semi-urban regions of Nepal (DKTI). Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.aepc.gov.np/pages/DKTI
- PV Magazine International. (2024, June 20). Nepal opens tender for grid-connected solar projects. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.pv-magazine.com/2024/06/20/nepal-opens-tender-for-grid-connected-solar-projects/
- International Water Management Institute. (2023, November). Grid-connected solar irrigation in Nepal – Exploring opportunities and identifying hurdles. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://solar.iwmi.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/43/2023/11/issue-brief-06-1.pdf
- Energypedia. (2023). Solar Pico PV market potential in Nepal. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://energypedia.info/images/a/a5/Solar_Pico_PV_Market_Potential_in_Nepal.pdf
- Worldsalaries.com. (2024). Average solar energy systems engineer salary in Nepal for 2024. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://worldsalaries.com/average-solar-energy-systems-engineer-salary-in-nepal/
- Worldometer. (2024). Nepal population. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/nepal-population/
- NepalSpace Property Solutions. (2024). Warehouse/store/godam archives. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://nepalspace.com/property_type/warehouse-store-godam/
- Regus. (2024). Office space for rent in Nepal | Serviced office. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.regus.com/en-us/nepal
- International Energy Agency. (2024). Nepal – Countries & regions. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.iea.org/countries/nepal
- Asian Development Bank. (2022). SSA: Nepal: Electricity transmission expansion and supply improvement project. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.adb.org/sites/default/files/linked-documents/41155-013-nep-ssa.pdf
- Observatory of Economic Complexity. (2024). Nepal (NPL) exports, imports, and trade partners. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://oec.world/en/profile/country/npl
- Lexology. (2024). The legal framework for renewable energy in Nepal. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.lexology.com/library/detail.aspx?g=108a58c2-be2c-43a9-a6e3-5441557553d0
- International Energy Agency. (2024). Renewable energy subsidy policy of Nepal – Policies. Retrieved December 10, 2024, from https://www.iea.org/policies/6228-renewable-energy-subsidy-policy-of-nepal