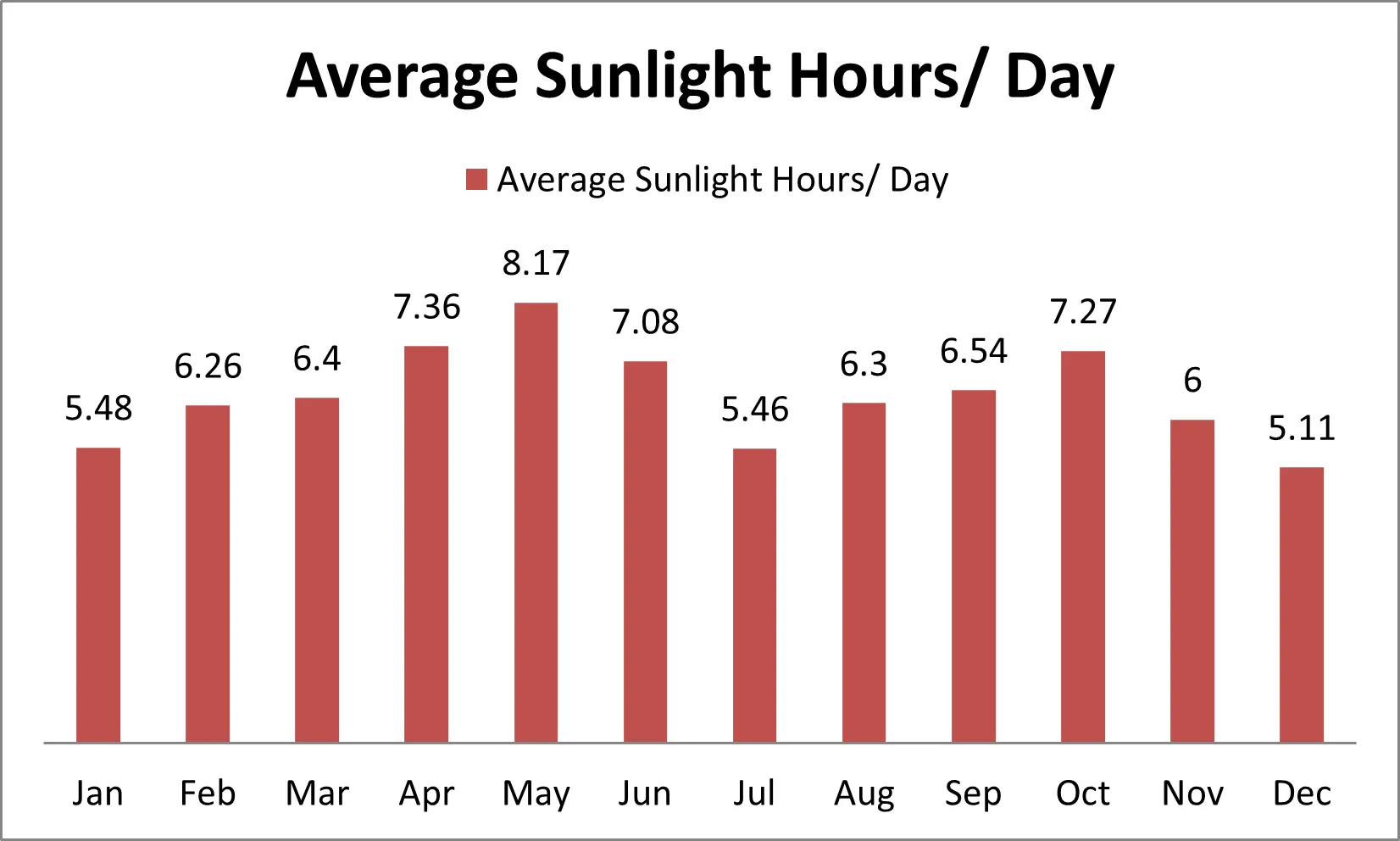
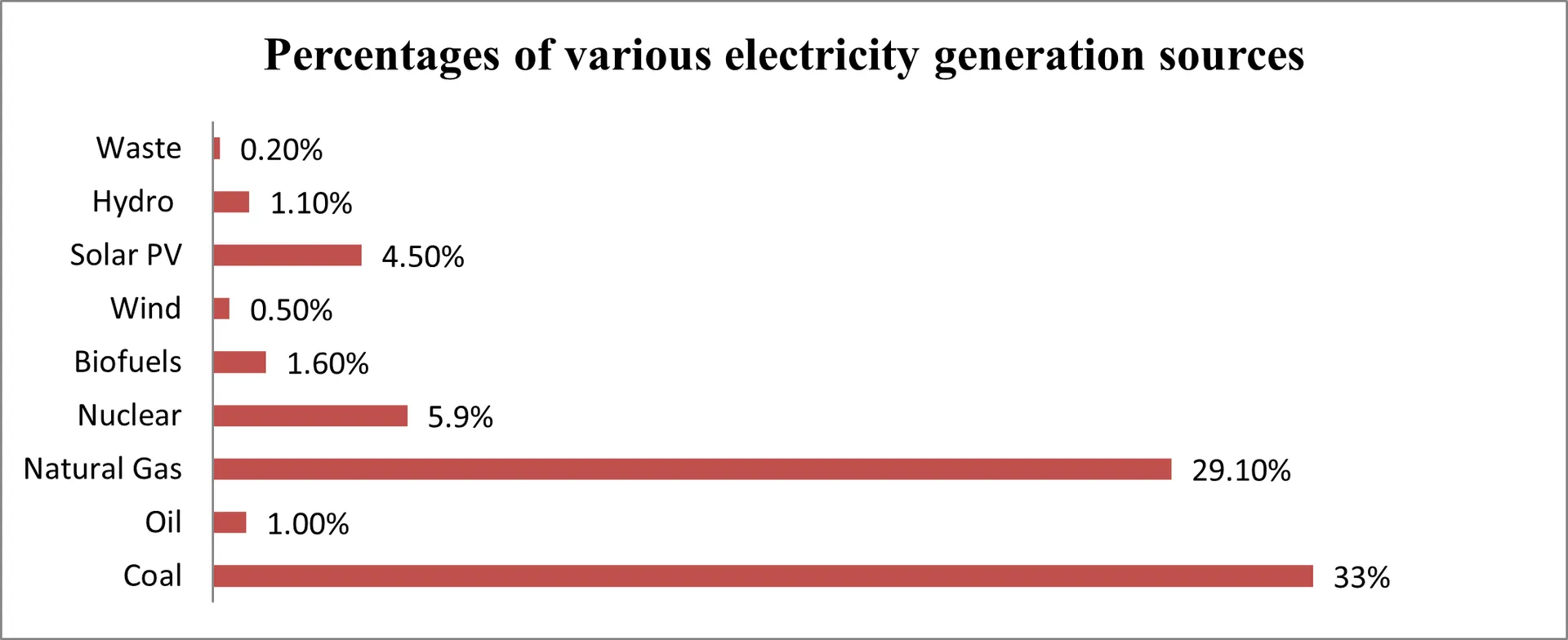
Discover comprehensive insights into the statistics, market trends, and growth potential surrounding the solar panel manufacturing industry in South Korea
- Climate Top. (2024). Sunshine & daylight hours in Seoul, South Korea. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.climate.top/south-korea/seoul/sunlight/#:~:text=There%20is%20an%20average%20of,haze%20or%20low%20sun%20intensity
- Lee, H.-S., et al. (2019). Analysis of power generation characteristics of a photovoltaic system in Korea. Korean Solar Energy Society. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.ksesjournal.co.kr/articles/article/DbW0/
- Statista. (2024). System marginal price (SMP) for the electricity market in South Korea from January 2017 to March 2023. Retrieved June 16, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1388776/south-korea-electricity-market-system-marginal-price/
- Sinalda. (n.d.). Voltage in South Korea. Retrieved June 16, 2024, from https://www.sinalda.com/world-voltages/asia/voltage-south-korea/
- Statista. (2024). Newly installed capacity of solar power generators in South Korea from 2018 to 2023. Retrieved June 16, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1386183/south-korea-newly-installed-solar-plants-capacity/
- Statista. (2023). Solar energy – South Korea. Retrieved June 16, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/outlook/io/energy/renewable-energy/solar-energy/south-korea
- ETN News. (n.d.). 3x increase in wind, solar to 72 GW by 2038. ETN News. Retrieved June 16, 2024, from https://etn.news/buzz/south-korea-triple-wind-solar-to-72-gw-2038
- Statista. (2024). Levelized cost of electricity calculator. Retrieved June 16, 2024, from https://www.iea.org/data-and-statistics/data-tools/levelised-cost-of-electricity-calculator
- IEA 50. (n.d.). Sources of electricity generation in Korea. International Energy Agency. Retrieved June 16, 2024, from https://www.iea.org/countries/korea/electricity
- International Energy Agency. (2022). National survey report of PV power applications in Korea 2022. Retrieved June 16, 2024, from https://iea-pvps.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/IEA-PVPS-National-Survey-Report-KOREA-2022.pdf
- Solarfeeds. (2022). Solar energy outlook on South Korea. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.solarfeeds.com/mag/solar-energy-outlook-in-south-korea-2022/
- PV Magazine. (2023, January 6). South Korea moves forward with long-expected solar panel recycling scheme. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.pv-magazine.com/2023/01/06/south-korea-moves-forward-with-long-expected-solar-panel-recycling-scheme/
- GlobalData. (n.d.). Solar PV and offshore wind power key for South Korea to achieve clean energy goals, opines GlobalData. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.globaldata.com/media/power/solar-pv-offshore-wind-power-key-south-korea-achieve-clean-energy-goals-opines-globaldata/
- REN21. (n.d.). Home page. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.ren21.net/
- Catalyze. (2024, January 22). South Korea industry trends. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://catalyze.com/2024/01/22/solar-industry-trends-south-korea-2024/
- Business and Finance World. (2024). South Korea Solar Energy Market Share 2024 Size Trends Growth Key Players. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://menafn.com/1107961225/South-Korea-Solar-Energy-Market-Share-2024-Size-Trends-Growth-Key-Players-And-Report-By-2032
- World Salaries. (n.d.). How much does a solar photovoltaic installer make in South Korea? Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://worldsalaries.com/average-solar-photovoltaic-installer-salary-in-south-korea/
- Worldometer. (n.d.). South Korea population. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.worldometers.info/world-population/south-korea-population/
- Hassan, M. (n.d.). Renewable energy in South Korea. CMS Law. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://cms.law/en/int/expert-guides/cms-expert-guide-to-renewable-energy/south-korea
- Power Technology. (n.d.). Solar PV in South Korea. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.power-technology.com/data-insights/solar-pv-in-south-korea/?cf-view
- Statista. (2023). Average monthly rental price for multi-owned commercial buildings in South Korea as of 1st quarter 2023, by province. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1304675/south-korea-rental-price-for-aggregate-commercial-buildings-by-province/
- Global Petrol Prices. (n.d.). South Korea electricity prices. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.globalpetrolprices.com/South-Korea/electricity_prices/
- RVO.nl. (2022). New solutions for water resources management in South Korea. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://data.rvo.nl/sites/default/files/2022/03/Water-Report-New-solutions-for-water-resources-management-in-South-Korea%20DEF.pdf
- Statista. (2023). Rental prices of office buildings in South Korea in 3rd quarter 2023, by province. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/statistics/1249017/south-korea-office-rental-prices-by-province/
- Statista. (n.d.). Property insurance – South Korea. Retrieved June 17, 2024, from https://www.statista.com/outlook/fmo/insurances/non-life-insurances/property-insurance/south-korea
- Indexbox (2024). Republic of Korea – Articles of Stationary – Market Analysis, Forecast, Size, Trend and Insight . Retrieved 11, Nov, 2024 from https://www.indexbox.io/search/stationery-price-south-korea/