A Strategic Analysis of Bahrain’s Business Environment for Solar Manufacturing
As the global energy landscape shifts, the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) has become a focal point for renewable energy investment. While larger nations often capture the headlines, the Kingdom of Bahrain presents a unique and compelling case for entrepreneurs and investors in the solar manufacturing sector. The country’s strategic vision, pro-business policies, and targeted approach foster a stable and promising environment for a solar production facility.
This analysis takes a clear-eyed look at Bahrain’s business climate, examining its economic framework, government incentives, and the practical considerations for investors evaluating the country as a manufacturing base.
Table of Contents
Bahrain’s Pro-Business Framework: A Foundation for Growth
Bahrain has earned its reputation as one of the most open and liberal economies in the Middle East—a reputation built on a long-term strategy outlined in its Economic Vision 2030, which prioritizes diversification away from oil and gas. For solar manufacturers, this translates into a stable and predictable environment with several key advantages.
The government actively encourages foreign investment by allowing 100% foreign ownership of businesses in most sectors, including renewable energy manufacturing. This policy removes a significant barrier to entry found in other regional markets.
Bahrain also operates in a tax-free environment, with no corporate, personal income, or capital gains taxes. This financial structure allows manufacturers to reinvest more capital into growth, technology, and operational excellence.
The process is facilitated by the Bahrain Economic Development Board (EDB), a government agency serving as a single point of contact for investors. The EDB provides comprehensive support—from navigating company registration to identifying strategic opportunities—significantly streamlining the setup.

The National Renewable Energy Action Plan (NREAP)
Bahrain’s commitment to solar energy is formalized through its National Renewable Energy Action Plan (NREAP). The plan sets clear, achievable targets, giving investors a transparent roadmap for the country’s direction.
Key goals:
- 5% of total energy from renewables by 2025.
- 20% renewable energy share by 2035.
To meet these targets, the NREAP outlines several large-scale projects, including a 100-megawatt solar farm on the Askar landfill and a 50-megawatt initiative for solar panels on government building rooftops.
Recent installations, such as the 11,600 rooftop panels at Bahrain Mall, demonstrate the viability of and government backing for such initiatives. This pipeline of projects creates solid domestic demand for solar modules, giving new manufacturers an immediate local market.
Curious about solar?
Dive into our free e-course for essential insights or get direct, expert assistance with our specialized services. We’re here to ensure your entire solar journey is seamless and successful.
Bahrain’s Competitive Edge in the GCC
While larger GCC nations offer scale, Bahrain provides distinct advantages—particularly for small to medium-sized manufacturers or new market entrants. Its primary edge lies in operational efficiency and market access.
Operationally, the cost of doing business in Bahrain is highly competitive, with labor costs, utility rates, and industrial land prices often lower than in neighboring commercial hubs. This advantage, combined with the country’s tax-free status, results in lower overall operational expenditures—a critical factor for any manufacturing business.
Strategically, Bahrain is an ideal gateway to the wider GCC market, especially Saudi Arabia, the region’s largest economy. The King Fahd Causeway provides direct road access, simplifying logistics and cutting transportation costs for exporting finished solar modules. Bahrain’s free trade agreement with the United States offers another key advantage for manufacturers targeting North American markets.
Setting Up a Solar Manufacturing Facility: Practical Steps
Establishing a manufacturing business in Bahrain is an efficient process; company registration can often be completed within days through a streamlined digital portal.

The first step for investors is to choose a legal structure, such as a Limited Liability Company (W.L.L.), a common choice for foreign entities. Next, investors must secure the necessary licenses and permits from the relevant ministries. The Ministry of Industry and Commerce oversees primary business registration, while specific approvals related to energy and the environment may be required.
Once the legal framework is in place, the next step is securing a suitable location. Bahrain offers several industrial zones with developed infrastructure, power, and logistics support designed for manufacturing operations. The EDB can help identify the most suitable sites based on an investor’s specific needs.
Navigating Potential Challenges
Every investment destination has its challenges, and in Bahrain, a primary constraint is land scarcity due to its small size. This has led to a strategic focus on rooftop installations and innovative solutions like floating solar, a key growth area in the wider GCC floating solar panels market. For manufacturers, this means the market may favor specific module types designed for distributed generation over those for utility-scale, ground-mounted projects.
While Bahrain’s renewable energy sector is growing, it also faces competition from established manufacturers in the wider region. A successful strategy will require a clear value proposition—whether that means focusing on a specific technology niche, superior quality, or leveraging Bahrain’s logistical advantages to serve export markets efficiently.
The Long-Term Outlook for Solar Manufacturing
Bahrain’s vision for a sustainable future extends beyond its 2035 targets, as the country positions itself as a hub for clean technology innovation in emerging sectors like green hydrogen. For a solar manufacturer, a presence in Bahrain means becoming part of a growing ecosystem focused on the future of energy.
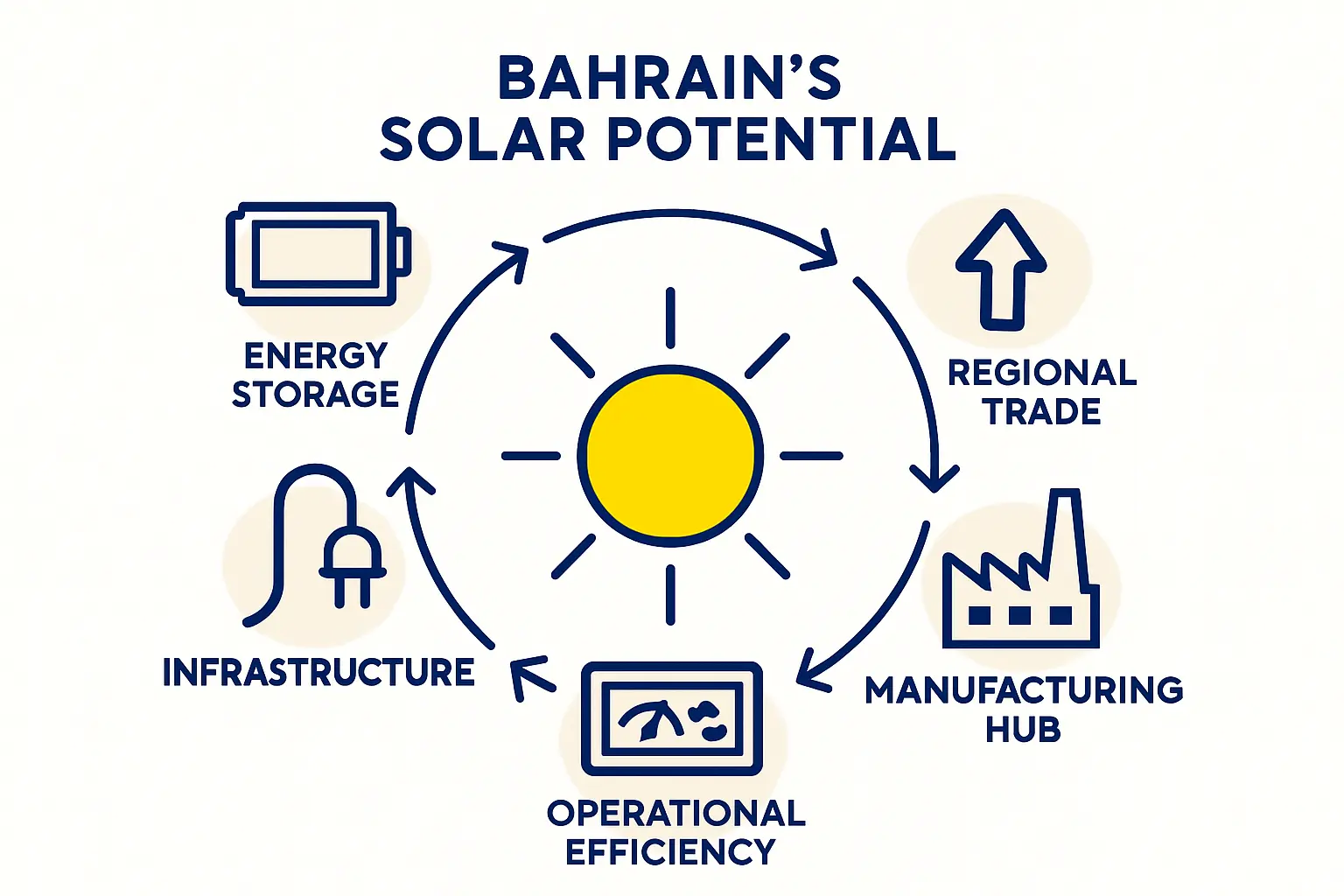
The combination of strong government backing, a stable, tax-free economy, and strategic market access makes Bahrain a highly attractive location for solar manufacturing. For entrepreneurs ready to build a local, independent solar production facility, Bahrain offers the clarity, support, and framework to turn an idea into a factory.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are Bahrain’s official renewable energy targets?
Bahrain aims to generate 5% of its energy from renewable sources by 2025, with a target of 20% by 2035, as outlined in its National Renewable Energy Action Plan (NREAP).
Can a foreign investor own 100% of a solar manufacturing company in Bahrain?
Yes, Bahrain allows 100% foreign ownership in the renewable energy sector and most other industries, providing full control over your investment.
What is the corporate tax rate for a manufacturing business in Bahrain?
Bahrain has a zero-tax policy. There are no corporate income taxes, personal income taxes, or capital gains taxes, which significantly enhances financial returns for businesses.
What kind of support does the Bahrain Economic Development Board (EDB) offer?
The EDB acts as a partner for investors, providing support throughout the setup process. This includes guidance on legal and regulatory requirements, assistance with site selection, and facilitating connections with government bodies and local partners.